Specializing Word Embeddings (for Parsing) by Information Bottleneck
どんな論文?
Information Bottleneckを使用して、ELMOをparsingに特化したベクトルに変換する手法。
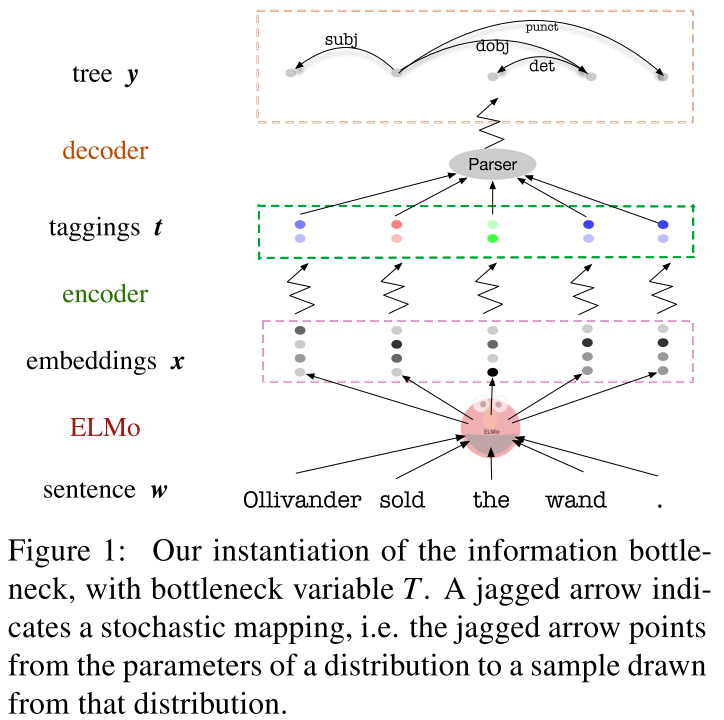
新規性
- information bottleneckを使って、embedingを特化させる点
- 推定方法の色々な工夫
- parsingの部分だけを取り出すため、layer-0の相互情報量で、正規化
結果
- bottle-neckに閾値があり、ある点から急に精度が下がる。
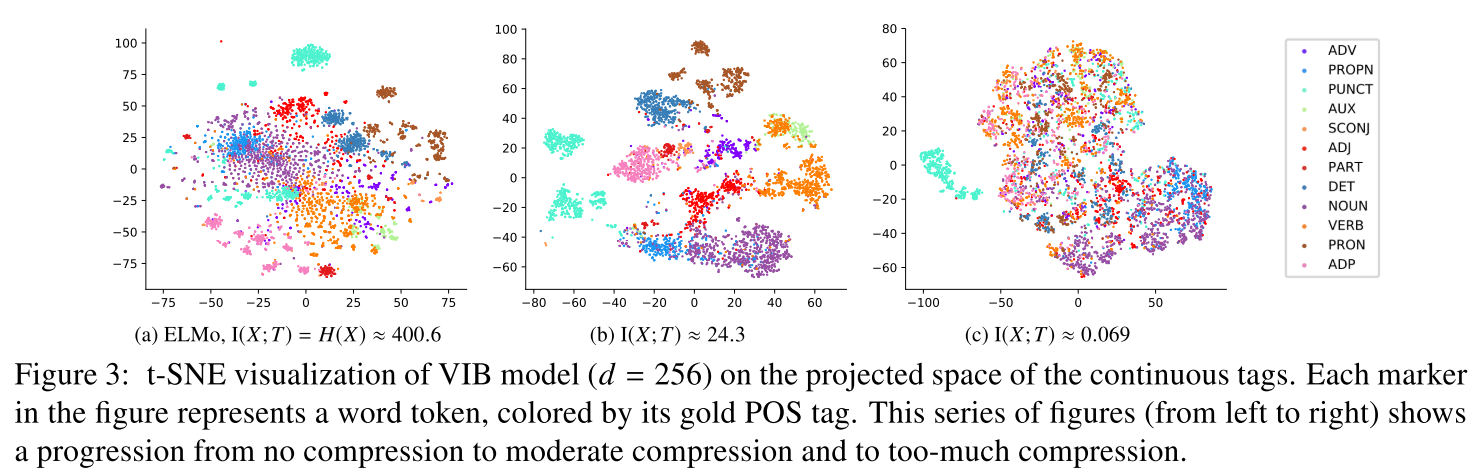
- 適度に絞ると、posタグごとに分散表現が別れる(fig2)
- 離散的なタグをbottle-neckにすると、posタグと相関がある
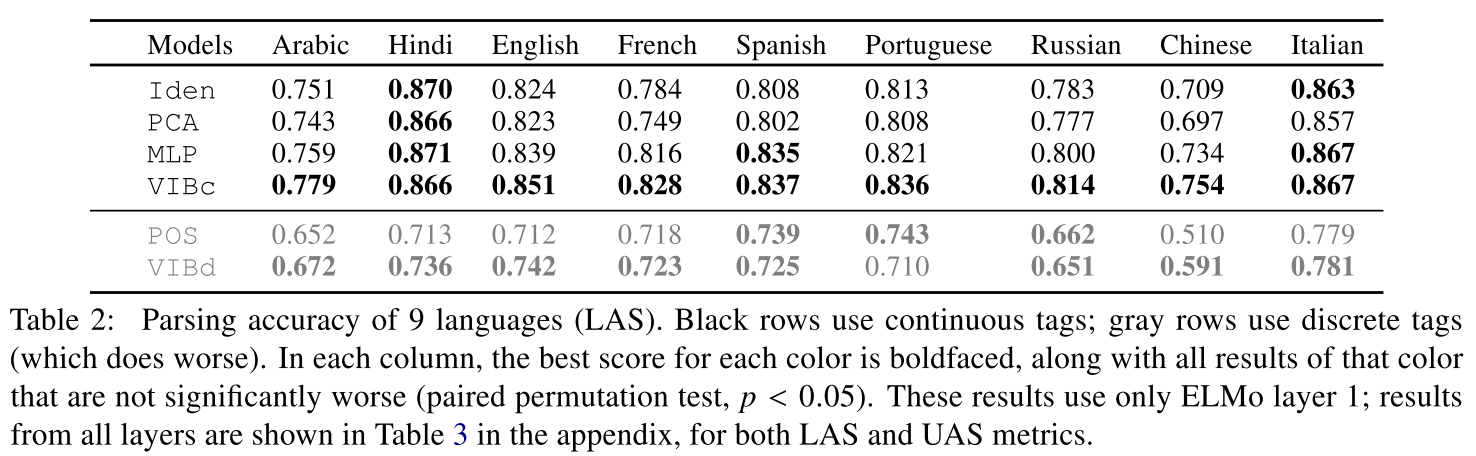
- ELMOそのままや、他の圧縮手法に比べ、parsingの精度が9言語中8つで向上した。(table1)
次に読むべき論文
- 推定方法
- Alexander A. Alemi, Ian Fischer, Joshua V. Dillon, and Kevin Murphy. 2016. Deep variational infor mation bottleneck. Proceedings ofthe International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR)
- Ben Poole, Sherjil Ozair, A¨aron van den Oord, Alexan- der A. Alemi, and George Tucker. 2019. On variational bounds of mutual information. CoRR, abs/1905.06922.
- IBの性質
- Naftali Tishby and Noga Zaslavsky. 2015. Deep learn ing and the information bottleneck principle. 2015 IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), pages 1– 5.
- contextualized word vectorの性質
- Ian Tenney, Patrick Xia, Berlin Chen, Alex Wang, Adam Poliak, R. Thomas McCoy, Najoung Kim, Benjamin Van Durme, Samuel R. Bowman, Dipan- jan Das, and Ellie Pavlick. 2019. What do you learn from context? Probing for sentence structure in con textualized word representations